What are its chemical components?
Cannabis consists of 2 main ingredients, including THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) and CBD (cannabidiol).
THC acts on the CB1 and CB2 (cannabinoid receptors 1 and 2). CB1 is located mainly in the brain and CB2 is located at the periphery in the immune system. The endocannabinoid system is in normal human but it was found later after cannabis. That is why we called its name after cannabis. Its function is to control balance in our body, regarding emotion, appetite, sleep, and pain. Our endicannabinoid system consists of anandamide (AEA) and arachidonylglycerol (2-AG).
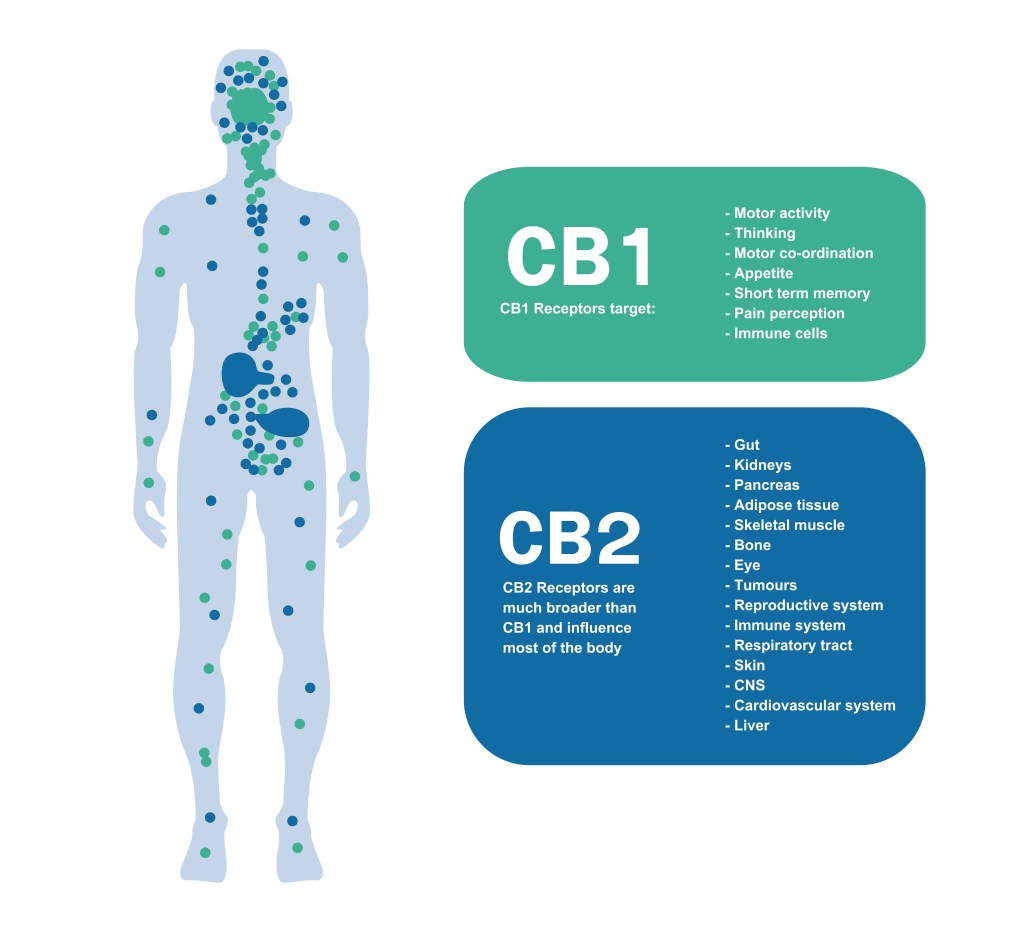
(WuttikitStudio/shutterstock.com)
We all have neurons which are cells in the nervous system. These cells communicate with each other by snapse which occur at a pore between two neurons. Normally, neurotransmitters are secreted from presynaptic neurons in to postsymaptic neurons. But endocannabinoid system acts in reverse, AEA and 2-AG are secreted from post synpatic nerurons into receptors in presynaptic nerurons, we called it retrograde signaling. This process inhibits neurotramsmitters secretion. This action can cause you to have effects of cannabis.
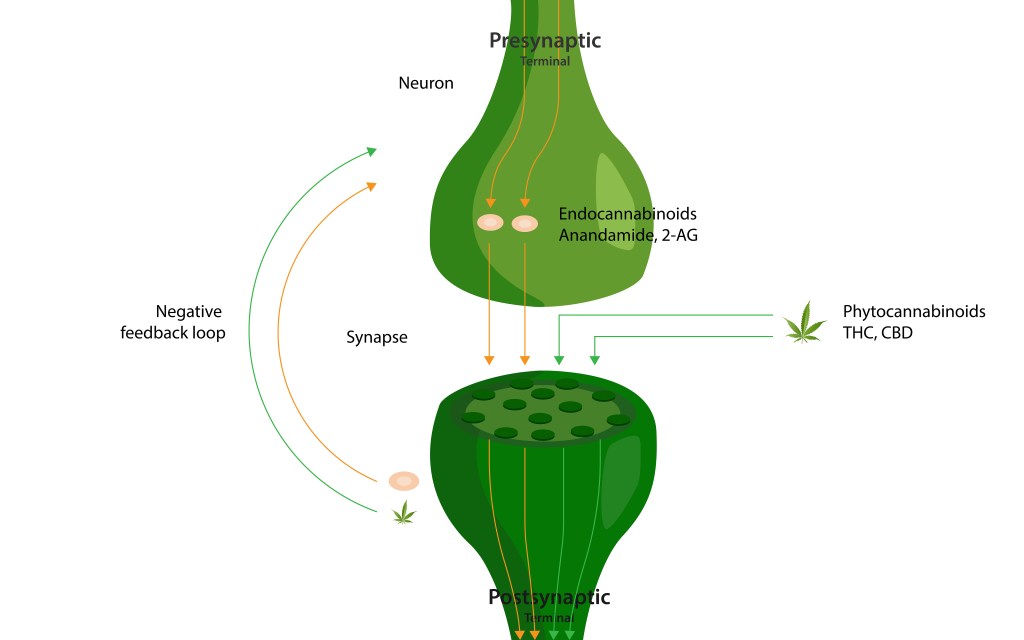
(About_time/shutterstock.com)
THC is more potent than endocannabinoid in our body and is mainly touch in CB1 receptors which are mainly in our brain. This is why we are high after taking cannabis.
CBD on the other hand, is not very potent with the CB1 receptors, but act on the CB2 receptos, which can reduce inflammation and pain. CBD can also act on the GABA receptors and increases its effect, which in turn, reduce anxiety and seizure.
What are cannabis strains?
Two main cannabis strains are Santiva and Indica. We characterize them by the shape of their leaves and trunks. In the past, we had research that found people who use Santive would experiece stimulation and people who use Indica would experiece relaxation or into the couch. The recent research showed that they are variation of THC and CBD between Santiva and Indica. Another compound that might cause the difference is Terpence which is oil that make smell of the cannabis.
Hemp is a type of cannabis that has less THC. We use this plant for the CBD mainly. This will produce less high effect or no effect of the THC.
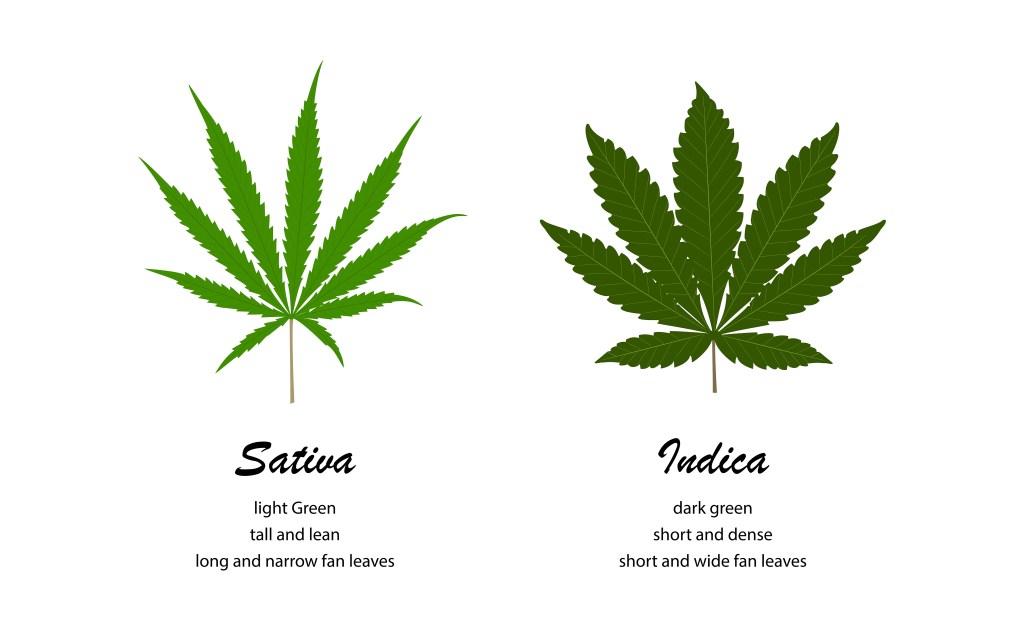
(About_time/shutterstock.com)
How can we consume cannabis?
We can use cannabis through multiple ways, namely smoking, vaping, eating, drinking, or cream applying.
Smoking is the fastest way for cannabis to take effects. When you smoke cannabis, it goes through your lungs and enter your blood stream promptly. The peak effect takes about 2-10 minutes.
Eating takes time longer. Cannabis will goes to your stomach and then get metabolized at your liver. This process will change the molecules of the cannabis and can make people feel different from smoking. The peak effect of eating cannabis is anout 1-3 hours.
What are the benefits of cannabis?
Recreational use
Cannabis can help people relax and socialize if you use recreationally. Some people might experiece happiness and increased joviality.
Cannabis can help you sleep faster, but it make your REM (rapid eye movement) sleep shorter. This means that you will dream less. However, chronic use can cause tollerance, therefore you may need higher dose to achieve the same effect. Suddenly stop cannabis can also worsen your sleep as well.
Medical use
Pain relief. THC and CBD reduce neurotransmitter secretion, therfore reduce pain. CBD can help pain via GABA secretion as well.
Antiemitics. Cannabis can help reduce vomitting, especially in patients with cancer who undergoing chemotherapy. THC can also stimulate Ghrelin which is a hormone that cause increased appetite.
Antiepileptics. THC and CBD can help patients with epilepsy who do not response to standard epileptic drugs. CBD can be used without high effect. There is a cannabis strain that is created with very high CBD and low THC. It was named after the patient who reponded well after CBD, Charlotte’s Web.
Anticancer. Due to CBD effect to the CB2 receptor in immune system. It can kill cancer cell in tests in animals,the evidence in human is still inclonclusion. It can help in some studies but also worse in others. CBD can also worsen outcomes in patients who recieving immunotherapy. ASCO (American society of clinical oncology) recommends agianst cannabis in cancer treatment.
What are the side effects of cannabis?
Addiction. Around 10% of cannabis users become addicts. This could be explained by the dopamine secretion from the THC. The addiction can show in various occasions, including increasing dosage of cannabis overtime, worsening work performance due to cannabis consumtion, or cannot stop using cannabis if they want to.
Cannabis has low chance to cause psychosis or aggravate underlying schizophrenia. This is unpredictable and can only be known if the person try cannabis. If you experience paranoid or delusion after using cannabis, you may need to stop.
Brain effects in adolescents. Normal brain can be developed until the age of 25. Cannabis can cause cerebral cortex to decrease its size, therfore it makes people less intelligence and worsen cognitive function in longterm. If you are under the age of 20, you should not be using cannabis.
Effects in pregnancy and lactation. Cannabis can go through the placentae in pregnant women and cause small gestational age in fetuses. It can also cause brain damage as well as in adolescents or much more worse. In lactating women, cannabis can pass through breast milk as well. It is strogly reccomended to not use cannabis in pregnancy and lacation women.
References:
McPartland JM, Small E. A classification of endangered high-THC cannabis (Cannabis sativa subsp. indica) domesticates and their wild relatives. PhytoKeys. 2020 Apr 3;144:81-112. doi: 10.3897/phytokeys.144.46700. PMID: 32296283; PMCID: PMC7148385.
Mouhamed Y, Vishnyakov A, Qorri B, Sambi M, Frank SMS, Nowierski C, Lamba A, Bhatti U, Szewczuk MR. Therapeutic potential of medicinal marijuana: an educational primer for health care professionals. Drug Healthc Patient Saf. 2018;10:45-66. https://doi.org/10.2147/DHPS.S158592.
Connor, J.P., Stjepanović, D., Le Foll, B. et al. Cannabis use and cannabis use disorder. Nat Rev Dis Primers 7, 16 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41572-021-00247-4.
Sholler DJ, Moran MB, Dolan SB, et al. Use patterns, beliefs, experiences, and behavioral economic demand of indica and sativa cannabis: A cross-sectional survey of cannabis users. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol. 2022;30(5):575-583. doi:10.1037/pha0000462.
Stella N. THC and CBD: Similarities and differences between siblings. Neuron. 2023 Feb 1;111(3):302-327. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2022.12.022. Epub 2023 Jan 12. PMID: 36638804; PMCID: PMC9898277.
Bergamaschi, M., Queiroz, R., Chagas, M. et al. Cannabidiol Reduces the Anxiety Induced by Simulated Public Speaking in Treatment-Naïve Social Phobia Patients. Neuropsychopharmacol 36, 1219–1226 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2011.6.
Braun IM, Bohlke K, Abrams DI, et al. Cannabis and Cannabinoids in Adults With Cancer: ASCO Guideline. J Clin Oncol. 2024;42(13):1575-1593. doi:10.1200/JCO.23.02596
Ortiz-Medina MB, Perea M, Torales J, Ventriglio A, Vitrani G, Aguilar L, Roncero C. Cannabis consumption and psychosis or schizophrenia development. Int J Soc Psychiatry. 2018 Nov;64(7):690-704. doi: 10.1177/0020764018801690. PMID: 30442059.
Albaugh MD, Ottino-Gonzalez J, Sidwell A, et al. Association of Cannabis Use During Adolescence With Neurodevelopment. JAMA Psychiatry. 2021;78(9):1031–1040. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2021.1258.
Corsi DJ, Donelle J, Sucha E, Hawken S, Hsu H, El-Chaâr D, Bisnaire L, Fell D, Wen SW, Walker M. Maternal cannabis use in pregnancy and child neurodevelopmental outcomes. Nat Med. 2020 Oct;26(10):1536-1540. doi: 10.1038/s41591-020-1002-5. Epub 2020 Aug 10. PMID: 32778828.
Paul SE, Hatoum AS, Fine JD, Johnson EC, Hansen I, Karcher NR, Moreau AL, Bondy E, Qu Y, Carter EB, Rogers CE, Agrawal A, Barch DM, Bogdan R. Associations Between Prenatal Cannabis Exposure and Childhood Outcomes: Results From the ABCD Study. JAMA Psychiatry. 2021 Jan 1;78(1):64-76. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2020.2902. PMID: 32965490; PMCID: PMC7512132.

Leave a comment